The structures of pathological TDP-43 aggregates are unknown
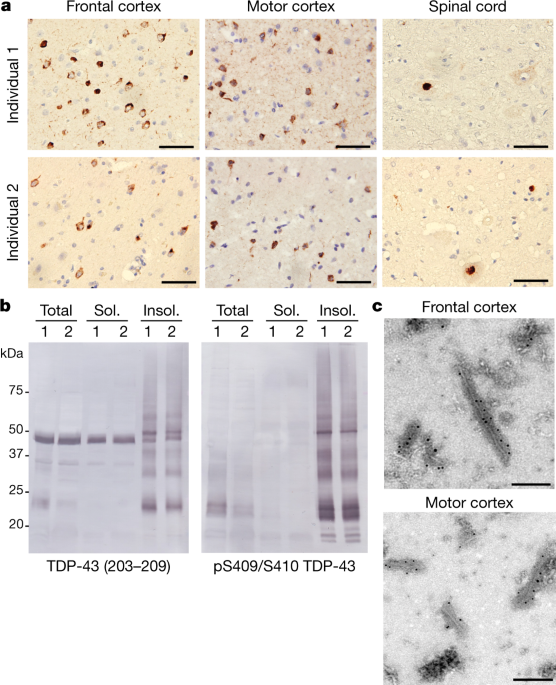
Here we used cryo-electron microscopy to determine the structures of aggregated TDP-43 in the frontal and motor cortices of an individual who had ALS with FTLD and from the frontal cortex of a second individual with the same diagnosis
The ordered filament core spans residues 282–360 in the TDP-43 low-complexity domain and adopts a previously undescribed double-spiral-shaped fold, which shows no similarity to those of TDP-43 filaments formed in vitro3,4
This work enhances our understanding of the molecular pathogenesis of ALS and FTLD and informs the development of diagnostic and therapeutic agents that target aggregated TDP-43
