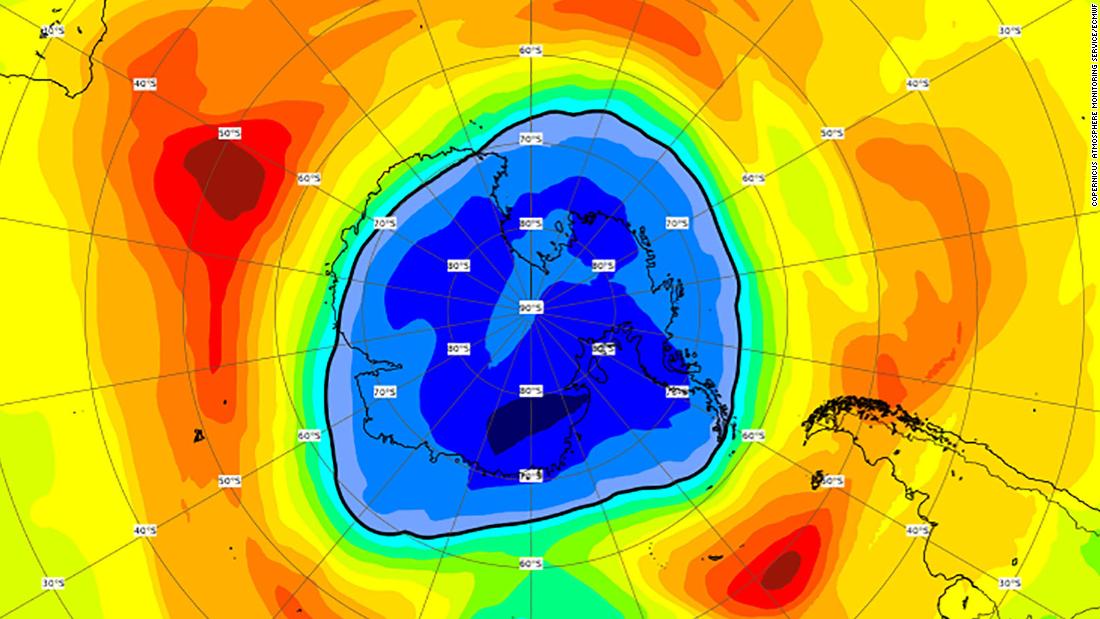
When temperatures high up in the stratosphere start to rise in the late spring, ozone depletion slows, the polar vortex weakens and finally breaks down, and by December, ozone levels usually return to normal.
This ends the isolation of air created by the polar vortex that forms during Antarctic winter, enabling chemicals such as chlorine and bromine to deplete the ozone layer, according to Copernicus and NASA.Ozone levels are usually restored to normal levels by December.
Copernicus monitors the ozone layer using computer modeling and satellite observations, and although the ozone layer is showing signs of recovery, Copernicus says it would not completely recover until the 2060s or 2070s.This is because it will take time to see the effects of the phasing out of chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), which deplete the ozone layer.The chemicals were first regulated by the Montreal Protocol -- first signed in 1987.