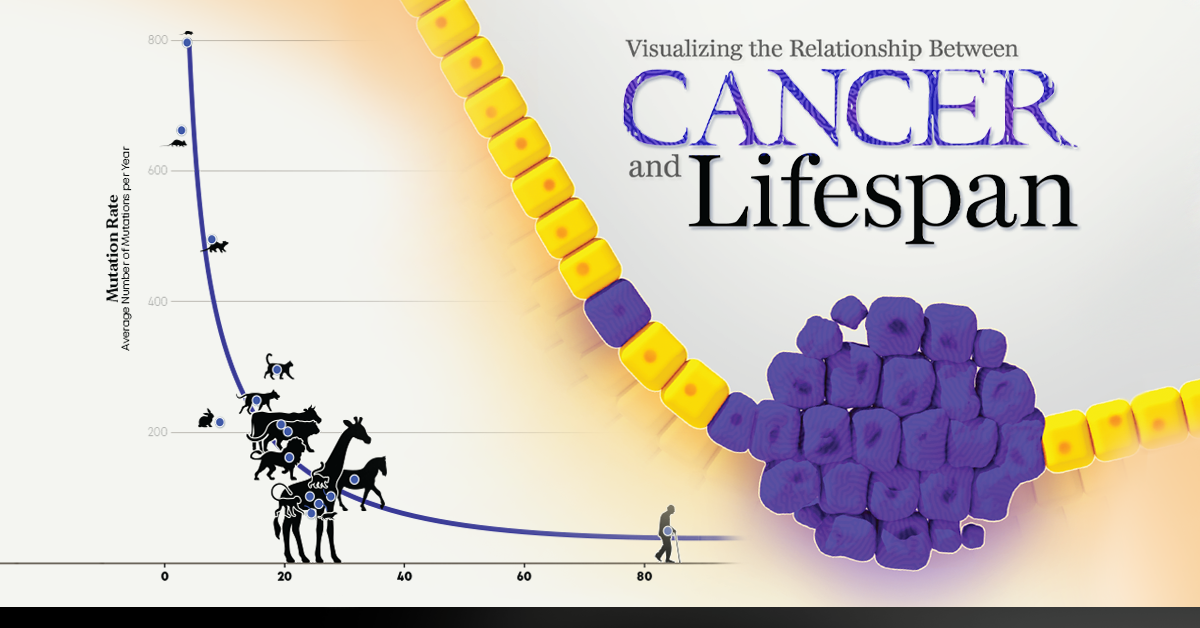
Mammals with shorter lifespans have average mutation rates that are very fast.
Mammals with longer lifespans have average mutation rates that are much slower.
The study also compares the number of mutations at time of death with other traits, like body mass and lifespan.Such small differentiation suggests there may be a total number of mutations a species can collect before it dies.Confirming that mutation rate and lifespan are strongly correlated needs comparison to lifeforms beyond mammals, like fishes, birds, and even plants.It will also be necessary to understand what factors control mutation rates.Geneticists and oncologists are continuing to investigate genetic curiosities like tumor-suppressing genes and how they might impact mutation rates.
Aging is likely to be a confluence of many issues, like epigenetic changes or telomere shortening, but if mutations are involved then there may be hopes of slowing genetic damage—or even reversing it.While just a first step, linking mutation rates to lifespan is a reframing of our understanding of cancer development, and it may open doors to new strategies and therapies for treating cancer or taming the number of health-related concerns that come with aging.Is it Possible to Bring Back Extinct Animal Species.Is it Possible to Bring Back Extinct Animal Species.This graphic provides an introduction to de-extinction, a field of biology focused on reviving extinct animal species.However, despite our many achievements in the realm of genetic engineering, one thing we’re still working on is bringing extinct animals back to life.In fact, there’s a whole field of biology that’s focused on reviving extinct species.
First thing’s first—what is the point of bringing back extinct animals.For instance, some scientists believe studying previously extinct animals and looking at how they function could help fill some gaps in our current theories around evolution.
That’s because when an animal goes extinct, its absence has a ripple effect on all the flora and fauna involved in that animal’s food web.
Because of this, reintroducing previously extinct species back into their old ecosystems could help rebalance and restore off-kilter environments.That’s why species like dinosaurs have virtually no chance of de-extinction.However, many organisms that went extinct more recently, like the dodo, could have a chance of conservation
There are several ways to do this, but in general, the process involves researchers manipulating the genomes of living species to make a new species that closely resembles an extinct oneBecause it’s not an exact copy of the extinct species’ DNA, this method will create a hybrid species that only resembles the extinct animalA form of breeding where a distinguishing trait from an extinct species (a horn or a color pattern) is bred back into living populationsLike genome editing, this method does not resurrect an extinct species, but resurrects the DNA and genetic diversity that gave the extinct species a distinguishing traitWhile there’s a ton of buzz and potential around the idea of bringing back extinct animal species, there are a few critics that believe our efforts would be better spent on other thingsIn an article in Science, Joseph Bennett, a biologist at Carleton University in Ottawa, said “if [a] billionaire is only interested in bringing back a species from the dead, power to him or her.”We show how the sizes of dinosaurs measured up
When dinosaurs inhabited the Earth over 66 million years ago, their sizes and species varied dramaticallyIn this infographic from Giulia De Amicis we compare the sizes of dinosaurs to get a sense of their vast scale and diversityWith access to virtual fossils, broad archeological datasets, as well as advancing techniques and new discoveries, the understanding of the sizes of dinosaurs continues to evolve